Setup
The program configuration is quite easy and done using a multiple dialog
(property sheet).
Packet Engine
Monitor
RadioPort Setup
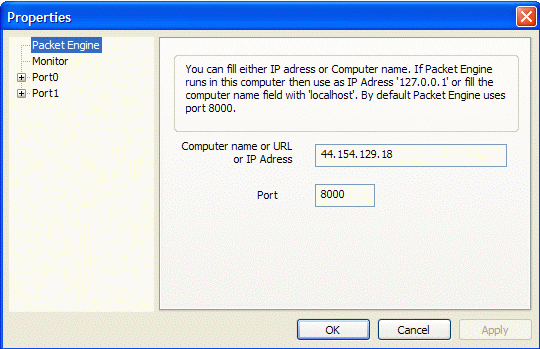
Packet Engine
.
Monitor
RadioPort Setup
You must configure each RadioPort separately.
Digi
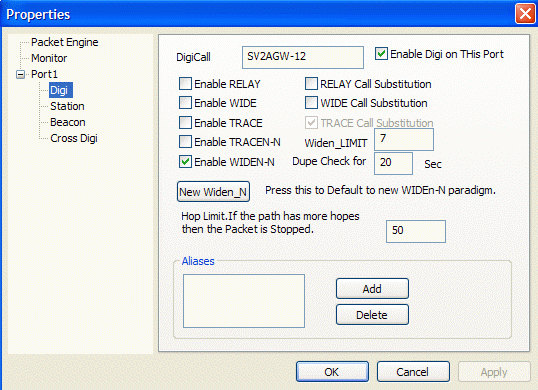
This is the digi setup dialog. Lets see how each
item affects the digi operation.
Enable RELAY.
If this is checked then the Digi will digipeat
packets that their via path (digi list) contains the
Call RELAY. All digis must digipeat these frames.
RELAY Call Substitution.
If this is checked then the digi will replace
the RELAY path call with its call. for instance the
frame
1:Fm SV2BBO to APAGW via RELAY
will become
1:Fm SV2BBO to APAGW via
SV2AGW-12* The RELAY call has been replaced
by Digi Call (SV2AGW-12).
Enable WIDE and WIDE Call Substitution
This controls if your digi will digipeat frames
that contain in the Via Path calls the call WIDE. In
most cases WIDE is enabled if your digi covers a
large Area and can be used to link different Packet
Areas. If your digi location is inside a city don't
enable it unless you are in a privilege position.
Call Substitution will replace the WIDE call with
your digi call and that way the Packet will not
propagate further.
Enable TRACE and Trace Call Substitution.
This controls if your digi will digipeat frames
that contain in the Via Path calls the Call TRACE.
By default the Call Substitution is enabled. Your
digi must digipeat these packets.
TRACEN-N and
WIDEN-N
AX25 specifications allow just 8 digipeaters in
the Via Path calls. This means that a Packet can do
just 8 hops from digi to digi. Although this seems
enough there are cases where you need your packet to
propagate further. WIDEN and TRACEN help to achieve
it. Lets see how it works. A packet with via path
set to WIDE5-5 is heard then the digi digipeats the
packet at replace the WIDE5-5 with WIDE5-4, other
digis that hear the WIDE5-4 decrease the SSID as
they digi it. When the SSID reaches zero then they
decrease the WIDE5 to WIDE4 and so on. That way this
packet can do 10 hops. YUou may specify a via path
like WIDE7-7,WIDE7-7 and so on. The TRACEN-N
works the same way but each time a digi digipeats a
frame inserts also its call. It mainly used to see
how a packet travels from digi to digi.
Dupe Check
Since the via Path of an APRS Packet contains
generic digipeater calls like WIDE,TRACE, RELAY etc
and to prevent retransmition of the same packet from
the same digipeater, we must have a mechanism to
prevent duplicate packet digipeating. AGWUIDigi has
a unique algorithm to check if a frame has been
digipeated. The list of digepated frames is kept in
memory for a time specified by the DupeCheck field
value. The algorithm works as follow. When a packet
received and digipeated the program calculates a
CRC32 value counting the bytes the information field
contains. That way frames with the same CRC32 are
ignored. A CRC32 value is removed from the list
after the specified time. This field contains the
time a CRC32 will be kept. It is in Seconds. A value
of 20 secs is enough.
NEW Widen-N
Pressing it setup digi on this radioport to
behave according to new Widen-N specifications for
USA. It actually stops any packet with a WIDEn-N
greater than 2. If a packet is received with say
Wide3-3 will be stoped. You can change this limit
from WIden-n Limit.
HOPS
You can set the MAX hops allowed. If a packet is
received with more than this limit Hops then it
stopped. For USA you must set it to 3. For other
countries set it to 14. If you set it to 14 then a
packet with a path of WIDE7-7,WIDE7-7 will be
digipeated.
Stopped Packets
A stopped packet is indicated with a path of QRT*.
That way the user may be notified that he uses a
very huge path and must lower it. It is more
politely than to ignore it.
Copyright 2004(SV2AGW) George Rossopoulos. All rights reserved.
|


