IZ8BLY Hellschreiber
For 32 bit Windows
© 1998-2004 Nino Porcino, nino.porcino@tin.it
http://iz8bly.sysonline.it
Release 4.0
IZ8BLY Hellschreiber is a Windows program
for transmitting and receiving Hellschreiber signals on
amateur radio bands. To learn more about this fascinating
mode, visit the Fuzzy
Modes web site. The IZ8BLY Hellschreiber
software is based on information from this web site, and on
other information from Murray ZL1BPU.
Table of Contents
IZ8BLY Hellschreiber is free software. You can copy it and
share it, so long as you don't charge any money for it, and
you don't modify it. If you pass the software on to others,
please pass on the original distribution file. Any commercial
distribution without the written permission of the author is
strictly prohibited.
If you use the program, please send some feedback, so that
the author can be encouraged to make improvements. Donations
would of course be welcome, but a friendly e-mail or postcard
will suffice. Contact the author at:
email: nino.porcino@tin.it
web: http://iz8bly.sysonline.it
or via snail mail:
Nino Porcino, IZ8BLY
Via dei Tulipani 21
89133 Reggio Calabria
ITALY - EUROPE
(If you want to meet Nino on air, try during weekends
(Sat-Sun) in Feld Hell mode, on 14063.5 KHz LSB around 13:00
UTC.)
Thanks go to the following people:
Murray ZL1BPU for all technical information and
for this help file
Paul PA0OCD and Vilnis YL2KF for constant on air tests and FB
QSOs
Peter G3PLX for help on the PTT routine and for the font file
Koos PA0KDF for original Hellschreiber font information
Lionel G3PPT for a great FFT waterfall display routine
Heinz DJ6SY for German help file translation
Josef OK2WO for Czech help file translation
Raimon EA3EZO for Spanish help file translation
Tapani Juhola OH2LU for French help file translation
Al WD5GNR for his PSKGNR PTT drivers
JA6AQV, JR6FQF and JA4HM of Kamnon-Yamaguchi SSTV Lab
for Japanese help file translation
Bob Furzer K4CY for integration with LOGGER
You will need:
- a computer with Windows 95™, Windows 98™,
or Windows NT™
- a 16 bit sound card that works with Windows
- an HF transceiver, preferably with VOX
- (optional) a Hamcomm interface or similar serial port
radio interface for PTT use.
Since you're reading this, you probably had no problem
installing the software! If you want to uninstall it, or
install a later version, use the Windows Control Panel. When
installing new releases of the program, you MUST uninstall
older ones first.
Connect the transceiver audio output to the line-in plug
of the sound card. Connect the audio output from the
soundcard to the transceiver microphone input, or auxiliary
input. Note that some transceivers will not provide VOX
operation from the auxiliary input. Isolation circuits
between the computer and the transceiver using small line
transformers are highly recommended. Use the Windows Control
Panel to adjust the input and output levels of your soundcard.
The Volume Control applet can be called from inside the
program - see later.
If you have internet access, a detailed installation
procedure is available at http://www.qsl.net/zl1bpu/FUZZY/IZ8setup.html,
on the "Fuzzy Modes" website.
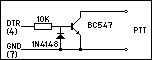
If VOX will not work with your transceiver,
you may need to fashion a PTT circuit as well. The
transmitter can be controlled by a signal from a serial port,
the DTR signal (pin 4) on COM1 to COM4. This is set in the File|Preferences
menu. The circuit required is an NPN open collector
transistor with a 10k base series resistor and a shunt diode.
This is the same as the PTT circuit of a simple "Hamcomm"
type interface often used for RTTY or SSTV, so if you already
have such an interface, it will save you building the circuit.
The IZ8BLY software uses the transceiver in
SSB mode. It does not matter whether you use Feld-Hell with
LSB or USB - which you use will depend on your filters and
whether you wish to chat to the other operator (helpful when
getting started). Some transceivers are easily modified to
use a narrow CW flter in SSB mode. If you don't have a
suitable narrow SSB filter on your receiver, you may want to
operate in split by receiving in CW (with a narrow
filter) and transmitting in SSB. If so, you will need to
allow for the CW sidetone shift when tuning the RX.
Some modes are sideband dependent.
These are C/MT-Hell, FSK-Hell and Duplo-Hell. The convention
is to use USB, so the higher tone is sent at a higher
frequency.
Press CTRL+P or choose "Preferences"
from the Menu to access the Preferences window. This window
has a series of tabs which you can click on to see various
mode related settings and alter them. The settings you choose
are stored in the IZ8BLY.INI
text file.
General:
- Callsign: used for the CW ID and CQ
calls
- Waterfall display: select how the
FFT display must be plot. If you choose the "log"
scale you will be able to see very weak signals,
intermodulation products and so on, but it may be
more difficult to tune because of the non sharp edges
of the Hell signal. "Linear" gives the
traditional black on white display with linear
response. You may want to disable the waterfall
display if you have a slow computer. In this case,
try first to increase the variable "BlockLenMultiplier"
in the IZ8BLY.INI file; it controls the CPU load and
program "fluidity".
- Slant Correction: If your soundcard
clock isn't accurate, you can correct it by entering
here a correction factor, to prevent slanted lines
when transmitting or receiving. This factor can be
calculated manually, or with a tool that requires you
to tune to a standard time and frequency station like
WWV (see the option "slant correction mode"
described later). The Slant Correction value
indicates the number of sampled data points that are
correctly processed by the soundcard before an error:
e.g. a value of 500 means that the soundcard
accumulates 1 error every 500 samples (at the sample
rate of 22,050 Hz). You can enter positive or
negative values depending whether your card is faster
or slower than it should be. Enter zero to disable
the slant correction. Before enabling the slant
correction, make sure it is YOUR card that is
inaccurate, because you will receive slanted lines if
another operator has an inaccurate soundcard. To be
certain, make a test with a standard time and
frequency station as described later.
- Idle character: The ASCII code of
the character to be sent when the TX is idle, i.e.
when you are completing a word with the keyboard, and
TX has to send something to preserve the phase
alignment with previous words sent. For example: if
the idle character is set to 32 it will send a space
character, 46 will send a dot and so on. By using a
visible idle character, slow typists and beginners
can show they are still there, have not stopped
transmitting, fallen asleep, or faded with the QSB...
- Min number of char in buffer: this
is the number of characters that can stay in the TX
buffer. If there are less characters than this number
an idle character is sent, otherwise the real
characters are sent. If you choose small values you
have a better behaviour when writing "long"
words (no idles are sent), but you'll have less
chances to correct a mistake because letters stay
less time in the buffer. Choose what is the best for
your typing speed.
- Center frequency (right click): let you define the sidetone
frequency to go to when pressing the right mouse button above
the waterfall display. Write here your IF narrowband filter's center
frequency (if you have any).
- Detect slow typing: This feature
will add an extra one-pixel column space between
letters when you are typing too slow in the TX buffer.
This helps to prevent the buffer becoming empty, by
increasing the duration of each character. At the
same time, the text becomes more readable because of
the extra space added. When the buffer is filled
suuiciently that there is no risk of an empty buffer,
the letters are transmitted normally again (without
the extra space column). Use this option to type at a
comfortable speed without worrying about whether the
buffer is empty and idle characters are sent
- Force uppercase. This option will
make sure that you send the text using uppercase
letters regardless of the caps lock key state. Lower
case letters are discouraged in Hellschreiber because
they do not respect the two-pixel rule and were not
included in the original Hellschreiber machine. They
are also difficult to read on DX, so it is better to
avoid them if possible.
- UTC Time in ADIF logfile: specify to use UTC format instead
of local format when generating the ADIF logfile.
- Computer Speed: this is used to
adapt the program performance to the computer's
calculation abilities. On slow PCs, some features
will be disabled or have lower performance.
- Line wrapping: Use to prevent text
being lost when it is split where it reaches the
right margin. Line wrapping copies a small portion of
the rightmost text onto the new line. Set the size of
this portion here (in pixels). The suggested value is
14 pixels (two Feld-Hell characters).
PTT:
- PTT Port: selects the method used to
key the transmitter on/off. Select "None"
to use VOX. If you use a Hamcomm-like interface,
specify the serial port where this is connected (COM1-4).
If you use a radio interface (CAT) it is possible to
use the PTT drivers used by the PSKGNR program by Al
Williams WD5GNR http://www.al-williams.com/wd5gnr/pskgnr.htm
or to use the LOGGER program by Bob Furzer K4CY.
- PSKGNR / LOGGER options: options to
use the PSKGNR drivers for or LOGGER program for
keying the transmitter. Program location is
the name of the executable file to be loaded if "Load
at startup" is checked. Close on exit
will unload it when exiting from the Hellschreiber.
- Beep when PTT off: The computer can
send a little "beep" from its internal
speaker when the transmission is complete. This is
useful if you are switching the TX manually, as you
will then know the right time to switch. If your beep
is redirected by Windows to the sound card, the beep
will be transmitted as well! In this case it is best
to leave the beep off, or disable the redirection.
Modes:
- CW Speed: the speed of CWID and CW
mode transmitting speed in words per minute (referred
to the word "PARIS")
- PSK Hell. In this mode one tone is
used, but the phase is reversed for every white dot,
and not reversed for every black dot. The normal Hell
adjustments are not applicable, so here you can use
the Display adjustment to set the
sharpness or smoothness of the received text.
Tools
- Log program: Here you specify the
command line for running your preferred log program.
The program will then be accessible via the menu
option "log program" (under the menu "Tools").
Use the "Browse" button to locate the
executable file to launch. You can also specify any
extra parameters needed, e.g. the archive file to
open etc...
- Mixer program: Specify here the
mixer program to be called when "Input volume"
and "Output volume" buttons are pressed.
The default program "SNDVOL32" is the
standard Windows volume utility. Change it if your
sound card uses another program (use the "Browse"
button to locate the executable file).
- PSK31 program: Specify here the
location of the PSK31 program, if you want to load it
quickly using the CTRL+K shortcut or via the menu (see
Menus below). Use the "Browse"
button to locate the executable file.
- MT63 program: Specify here the
location of the MT63 program by IZ8BLY, if you want
to switch to it using the CTRL+M shortcut or via the
menu (see Menus below). Use the
"Browse" button to locate the executable
file.
- Stream program: Specify here the
location of the Stream program by IZ8BLY, if you want
to switch to it using the CTRL+H shortcut or via the
menu (see Menus below). Use the
"Browse" button to locate the executable
file.
- Special macros: lets you customize
the text for the "CQ" button and the "F12"
button. When pressing F12, "preamble" is
the text sent to begin the transmission, "postamble"
to end it. You can use your own style or the classics
"european" and "oceanic" styles (respectively
"PSE K" and ">>").
Click on a menu item (or select with the normal Windows
keyboard ALT selections) to reach these controls:
FILE Menu
- Load Font (Ctrl+F) allows selection
of any suitable installed Windows font for the
transmitted characters. The font size should be 14 pt
or smaller. Smaller fonts will be faster, but more
difficult to read. Two different types of fonts are
offered: standard Windows fonts, and special Hell
fonts. Win98 and Win95 with PLUS! can render Windows
fonts as grey scale. With this "smooth
characters" option enabled, the greyed fonts can
be transmitted. The grey levels are sent by reducing
the transmitted power. Open the Control Panel Display
icon and click on the Plus! tab - check that "Smooth
edges of screen fonts" is ticked.
The Hell
fonts are special fonts which are designed to occupy
minimum bandwidth when transmitted, and to provide
very readable text. This is done by ensuring that the
14 dots per column are always transmitted at least
two at a time. Use these fonts for preference over
the Windows fonts, to conserve transmitted bandwidth.
The following Hell fonts are furnished with the
program:
| FELDHELL.FON |
The standard
Hell fontset made by G3PLX. It has only
uppercase letters. |
| FELDNARR.FON |
Like the
standard font, but 14% faster to send because
letters are spaced only one pixel (instead of
two). Includes both uppercase and lowercase
characters. Use it in good conditions and
only if you can type fast! Contains icons
characters. |
| FELDWIDE.FON |
The standard
font modified to be two pixels wider for
better readability under poor conditions.
Also useful for slow typists. It has both
uppercase and lowercase characters. |
| FELDLITL.FON |
A reduced
version of the standard font (only 4 pixels
wide), created for local chat qsos. Very fast
to send, but not readable under poor
conditions. |
| FELDFAT.FON |
A bold version of
the standard font with upper and lower case.
Very readable over DX. |
| FELD-DX.FON |
This is the
standard font, but with double width
characters in place of the lowercase letters. |
| FELDREAL.FON |
This is the
real font used by old mechanical
Hellschreiber machines. There is no lower
case, but when lowercase is attempted, this
font has one pixel spacing between characters
instead of the standard 2 pixel spacing (in
uppercase) |
| FELDLOW.FON |
This fontset
was obtained from the "Feldnarr.fon"
font by stretching and bolding it vertically.
It has a special property of minimum
bandwidth and a greater readibility over DX.
All characters are 2 pixels larger and, where
possible, never have less than 3-pixels
together on each vertical column. Contains
icons characters. |
| FELDVERT.FON |
This is a vertically
stretched version of the "Feldnarr.fon".
It has good readability and is the only font
where the lowercase letters follow the 2-pixel
rule. Contains icons characters. |
| FELDSTYL.FON |
An alternate version of
the previous "FeldVert.fon" |
| FELDMODERN.FON |
This a modern
version of the Feld Hell font, made to appear
like a font of the computer age. There are no
descending numbers and some weirdness from
the original font has been eliminated. |
| FELD7x7.FON |
A font that has the
resolution of a 7x7 font. It is automatically
used in PSK-Hell as it is the only font that
can be used in this mode. |
| FELD7x7n.FON |
A narrower (faster)
version of the FELD7x7 font. |
| SMTHELL.FON |
This fontset
is not intended to be used with Feld Hell,
but with S/MT Hell (not offered in this
version). It is a low resolution 5x7
proportional dot matrix font designed by
Murray ZL1BPU. |
It is recommended that you use the standard fonts
(FELDHELL or FELDNARR) because they best replicate
the traditional Hell font, which is still the best -
fast and easy to read. Many enthusiasts insist that
this special HELL font is one of the most important
features of Hellschreiber. It was cleverly designed
to be very readable when buried in noise, and each
character is uniquely identifiable without confusion.
In addition, the bandwidth used by the font is very
small, since although it was designed to have the
resolution of a 14 x 7 font, it behaves the same as a
7 x 7 font, since pixels or gaps between pixels are
never sent singly.
Note: A raised cosine envelope
processor is applied to the output signal of all
fonts of the "Feld" family. This reduces
the signal to minimum theoretical bandwidth. It is
not and cannot be used on Windows fonts, which can
make the transmission as much as four times as wide -
so use Windows fonts with care.
- Load palette. (Ctrl+L) Selecting
different (*.pal) palette files provides a choice of
different colours for the receiver display. These
files set the displayed RGB values for each of the
256 received dot levels. You can create your own
palette to provide different colours, contrast ratio
or gamma. The format of the palette file is simply a
list of 256 values in text format - see the default.pal
file as an example. The selection of palette has an
effect on the sensitivity to background noise, so
experiment for best results.
- Preferences (Ctrl+P)access the
preferences windows for configuration (see Configuration)
- Stand by (Ctrl+B)puts the program in
stand-by mode. The com port used for PTT and the
soundcard are temporary released to allow the user to
switch to another program (e.g. PSK31). The normal
execution is resumed when the user switches back
again to the Hellschreiber program.
- Exit closes the IZ8BLY program.
MODE Menu
Allows you select between:
TRANSMIT Menu
- Stop (Ctrl+X) stops the transmitter.
Continuing to type in the TX window will start it
again.
- Clear TX buffer (Ctrl+C) immediately
stops the transmission and clears the buffer.
- Send file (Ctrl+S) calls a dialog
for opening a text file and insert it in the text
buffer; e.g. you can store station information in a
file, and send it with a simple mouse click.
- Send CQ call (F9) will send a
standard CQ message.
- Send Tune signal (F8) will send a
full volume 980 Hz sinewave for tuning purposes. Use
it to adjust output volume and set out the total RF
power. Adjust your sound card so this signal is not
clipped.
- Send CW-ID (F10) will send the your
callsign in Morse for identification.
- Send pre/postamble phrase (F12)
sends a standard message for opening or closing an
"over" during a QSO. If not transmitting,
it will start with "RRR RRR <other> DE
<you>", it is useful also to have time to
type into the buffer to get ahead of the transmitter.
If transmitting, it will close the over with "<other>
DE <you> PSE KN". You can define your own
customized pre/postable messages in the Preferences
window (see above).
- Satellite mode: makes the Hellschreiber program work in full
duplex mode by letting the plot of own transmission. Use this if
you are working with satellites or if you have separated RX and TX and
want to monitor your output signal. Works only with true full-duplex
soundcards.
- Meteorscatter mode: this option modifies the the speed for
special applications. The slower speed (1/8X) is intended to be used
for QSOs via troposcatter. Faster speeds (5X, 9X and 10X) are for meteorscatter
where the signal is quite strong but lasts very little time (the bandwidth
increases proportionally, so use it with care). The 10X speed features
a special version of the Duplo Hell where a 4-FSK modulation (running
at 612.5 bauds) is used to encode two pixel at a time. The four tones
are spaced equally 612.5 Hz each other and the resulting signal
occupies the whole SSB bandpass. Note: in the 10X speed the frequency
display is meaningless and tuning must be done via the RTX's VFO.
RECEIVE Menu
- Start (Ctrl+R) starts the receiver
sampling and display process. Has the same effect as
the tool bar "Paper" button.
- Stop Stops the receiver. Has the
same effect as toggling the tool bar "Paper"
button.
- Tune to biggest signal: (Shift+F12)
tunes the receive and transmit tone to the strongest
signal displayed in the waterfall display. May be
useful if you don't use the mouse.
MACRO Menu
- this menu shows what are defined macros and the
shortcuts to run them. See the definable user button
below.
TOOLS Menu
- Pause Mode. This sets the "pause
mode" as default. Normally, when you type in the
transmit buffer, each word is transmitted as the word
is completed with a space. With this option turned on
you can type ahead without transmitting until you
press ENTER key. (You can just as easily employ
"pause mode" by typing an asterisk
character (*) as first character in the buffer.)
- Auto save bitmap snapshots. The
receiver can automatically save receiver bitmaps,
which are useful for reference or to email to the
stations you work. This option enables this feature,
which stores a 400k byte file in the \snapshots\
folder every two minutes at standard speed. File
names are created automatically from the date and
time. Please note: for sending by email, you must
reduce the image size, reduce the colours to 16, and
change the format to .GIF, which will reduce the file
size dramatically.
- Lookbook window (F11) allows you to
log the QSO's details. Each logged entry is written
to the file HELL.ADI wich is in ADIF standard format
that you can import into an external logging program.
If you have the LOGGER program by Bob Furzer K4CY
running in the background, the datas will be passed
automatically without importing them as ADIF file.
The main advantage of using the logbook window
instead of using an external logger program directly,
is that the name and callsign of the other party are
available as $OTHER and $OTHERNAME metacommands that
you can use in macros (see the complete list of
metacommands for reference). Use the key F11 to
switch between TX buffer and logbook window.
- Actual frequency calculator (Ctrl+A).
A simple tool to calculate on the fly the "actual"
frequency and/or the "dial" frequency. The
actual frequency is the frequency really transmitted,
that is NOT the frequency you read on your
transceiver display. In LSB or USB the dial frequency
differs from the actual frequency by +/- the sidetone
value. You should always refer
to the actual frequency since you can't know if the
other operator is using LSB or USB or another system
with different sidetone values. This tool also helps
you to change from LSB to USB (or vice-versa), for
example in order eliminate interference from an
adjacent signal.
- Slant correction mode is a tool that
lets you check and calculate the exact slant factor
for your soundcard clock . Tune your receiver to a
standard time and frequency station such as WWV, CHU
or JJY, using AM mode. You will find suitable
stations on 2.5, 5, 10, 15 and 20 MHz, as well as
other places in the HF spectrum. If you live in
Europe, try the Russian station RWM, which is very
easy to receive on 14996.98 KHz (LSB), MSF (59 kHz
LSB) or DCF77 (76 kHz LSB). Standard time and
frequency stations repeatedly send beeps at the
precise interval of one second; these sound beeps are
displayed by the program at the rate of one column
per second, so if your soundcard is precise, you will
see a perfectly horizontal line among the other marks.
If the line slants up or down, type a number or move
the arrows until you have the right correction factor,
that is, when you see a straight horizontal line. The
higher the value, the less the correction. Try values
around 400-500 for slight slanting, or around 100 for
serious slanting. Negative values are used if the
soundcard clock is running fast rather than slow.
When finished, click on "Close" to return
to normal Feld Hell. Use the "Reset" button
or write the value "0" to disable the slant
correction.
Notes: (1) standard time and frequency stations often
change the type of transmission used every hour. If
you do not hear the sound beeps, simply wait until
this occurs or try another station. (2) 1/10 sec.
beeps are good too (you will see many lines at the
same time). (3) This test is quite slow, so for very
accurate adjustment, leave the correction mode
running for at least 5 minutes. (4) Do not run other
software while the test is running, or there may be
steps in the timing line!
- Slowfeld receiver lets you receive
signals transmitted by Lionel G3PPT's SlowFeld
program. "Slowfeld" is transmitted the same
as normal Feld Hell, but the speed is drastically
reduced to only 2 characters per minute. It is used
maily for experimetal purposes.
- FM Shift Tester: this tool let you experiment with the
FM-Hell by testing very narrow shift values. Experiments with values
from 1.2 to 4. Enter 0 to return to normal shift value.
- Who is... (Ctrl+W) lets you quickly
search for a callsign in the "Hellschreiber Call
Book" database. Name, QTH, Locator, Email and
equipment used are shown if they are available.
Please send updates or corrections using the
appropriate page on the web, or by email directly to
the author (or tell him on-air if you meet him). You
can also keep your local database updated by simply
saving the Call Book webpage from internet in the
"Database" folder.
- View callbook opens the local hard
disk copy of the Hellschreiber Call Book.
- Log program: (Ctrl+G) launches your
external log book program (has to be previously
specified in the configuration window).
- MT63: (Ctr+M) puts Hellschreiber in
stand-by mode and switches to the MT63 program by IZ8BLY
specified in the Preferences window. This lets you a
quick switch, avoiding conflicts between the two
programs (as both use soundcard and serial port).
Note: in the MT63 program use CTRL+H to return to
Hellschreiber.
- PSK31: (Ctr+K) puts Hellschreiber in
stand-by mode and loads the PSK31 program specified
in the Preferences window. This lets you switch
quickly, avoiding conflicts between the two programs
(as both use soundcard and serial port). Before
returning to Hellschreiber, close the PSK31 program.
- Stream: (Ctr+H) puts Hellschreiber in
stand-by mode and switches to the Stream program by IZ8BLY
specified in the Preferences window. This lets you a
quick switch, avoiding conflicts between the two
programs (as both use soundcard and serial port).
Note: in the Stream program use CTRL+H to return to
Hellschreiber.
The Paper button is used to start and
stop the decoding of Hell signals, which will be displayed in
the Receive window. Once the bottom line of text fills, it
will be transferred up one line and the recording will start
at the beginning of the line again. The same button both
starts and stops the "virtual paper".
The Set Input/Output Volume buttons call
up the sound card mixer program to set input and output
volumes and ports. Make sure that the level does not
cause clipping in the transmitter. Setting the level too high
will not make the signal any stronger - it will just be
harder to read and cause more interference. Linearity
is especially important if transmitting grey scale characters
or raised cosine shaped signals. Note: With Win95 both
buttons generally launch the same Volume Control applet (Set
Output Volume), so on this applet use Options/Properties and
select Recording to Set Input Volume.
Preferences button calls the
configuration window.
Small/Big Letters display button doubles
the size of the text on the receive window making it more
visible.
DX Mode button. In DX mode, each column
of the transmitted characters is sent twice. This halves the
text speed, but significantly improves the resistance of the
text to noise, and characters will appear to be twice as wide
as normal.
Snapshot button will save the current
display into a bitmap file. You can use it instead of the
"Auto save bitmap snapshot" (see above).
AGC button: turns on/off the AGC
improving the readibility on weak signals.The AGC tracks the
signal peaks, and keeps the text at the optimum contrast. You
can adjust the behaviour of the AGC by moving the slider
"AGC response" (see later)
The Filter Bandwidth slider lets you
choose the bandwidth of the DSP filter which improves the
receiver performance for Feld Hell and CW. A narrow bandwidth
can eliminate undesidered signals, but the text will became
softer and more blurry.
AGC response let you modify the behaviour
of the AGC on weak signals. If the AGC is too fast it may be
influenced by impulse noises. If set too slow, you may miss
letters when the signal fades quickly. Experiment for best
results.
Logbook: opens / closes the logbook
window.
Frequency shows the center frequency of
Hellschreiber transmitter and receiver. You can modify it
directly or by clicking with the mouse on the waterfall
display.
The Receive Window displays a series of lines of double-printed
text. Each character is printed twice, once above the other.
This ensures that the text remains readable since the phase
of the received signal is unpredictable.
As a line is completed, the display is scrolled up,
beginning with a new line. When close to the right margin of
the line, words can often be split in two. To minimize this
problem the "line wrapping" option (described in
the configuration) can alter the amount of text replicated on
the new line.
The Transmit buffer is a single line
below the Receive Window, where the characters to be
transmitted are typed. Text will be sent whenever a word is
completed with a space character. Type ENTER when you finish
typing in the TX buffer, or the last word will not be sent
and the receiver will not restart. This is especially
important at the end of each over. If the "pause mode"
is enabled, or you type an asterisk (*) as the first
character, you can type during reception, and the text will
only be transmitted when the ENTER key is pressed.
You can also type metacommands into the TX buffer.
These are general purpose program commands and are denoted by
the dollar sign ($). They can be typed directly into the
Transmit Window, included in user definable buttons, or put
in a text file to be sent via a menu option.
| Metacommand |
Text sent / action taken |
| $QRZ |
The station callsign (typed in preferences window) |
| $OTHER |
The other party callsign (defined with F11 key) |
| $OTHERNAME |
The other party name (defined with F11 key) |
| $OTHERQTH |
The other party qth (defined with F11 key) |
| $OTHERRST |
The RST received by other party (defined with F11
key) |
| $RST |
The RST you have sent to the other party (defined
with F11 key) |
| $CQ |
Sends standard CQ call |
| $CWID |
Sends ID in Morse for countries where this is
required |
| $UTC |
Time stamp (UTC time) |
| $TIME |
Time stamp (local time) |
| $DATE |
Date stamp (referred to local time) |
| $DATEUTC |
Date stamp (referred to UTC time) |
| $$ |
The dollar sign (otherwise not printable) |
| $TUNE |
Sends a full volume sinewave for tuning purposes.
Use this to adjust the output volume or set the RF
power. |
| $IMD |
Sends a two carriers signal for visual
intermodulation (IMD) checks |
| $FELD |
Switches mode to Feld-Hell |
| $CW |
Switches to Morse mode |
| $CMT |
Switches to C/MT mode |
| $FSK105 |
Switches to FM Hell mode (105 baud) |
| $FSK245 |
Switches to FM Hell mode (245 baud) |
| $DUPLO |
Switches to Duplo Hell mode |
| $PSK105 |
Switches to PSK Hell mode (105 baud) |
| $PSK245 |
Switches to PSK Hell mode (245 baud) |
| $Cnn |
Sends ASCII character number nn, e.g. $c65 sends
"A" |
| $BUTTONn |
Sends text assigned to the user definable button
n (ranges is from 1 to 12) |
| $DXON |
Turns on DX mode (doubled columns) |
| $DXOFF |
Turns off DX mode (doubled columns) |
| $NOQSO |
Clears other party callsign ($OTHER). |
| $Pn |
Sets the output power level (soundcard volume) to
n.
The value ranges from 0 (silence) to 255 (full volume).
This metacommand influences the mixer setting. |
The user definable buttons are placed
below the transmit buffer. You can modify their content, and
the name on the button, by right clicking on the desired
button. You can store pre-defined phrases and metacommands,
then send them later by left clicking on the button or by
pressing the CTRL+FKey shortcut as shown above the button
itself.
Tune signal sends a full volume sinewave
for tuning purposes. Use this to adjust the output volume or
set the RF power.
IMD signal sends a two carriers signal
for visual intermodulation (IMD) checks. If the sound
transmitted is intermodulated the other party will be able to
see harmonic images of the two carriers. The more number of
harmonics, the more the intermodulation. If sound is set
correctly only two pure carriers should be visible.
The Tuning Display shows a waterfall plot of the received
signal, using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) technique. The
red line shows where the current receive and transmit
frequency is. Click with the pointer on the signal you want
to tune, or press SHIFT+F12 to tune to the maximum signal.
Use right mouse button to reset the frequency to center (1300
Hz). When transmitting, it not recommended to use too low or
too high frequencies, as many transceivers do not have a
linear response in the audio input.
Note: if you are overdriving the input of your soundcard,
the display will turn into red. In this case, use the "Input
Volume" button and decrease the "line in" or
"mic" volume as necessary.
IZ8BLY Virtual Hellschreiber Machine
| General |
| Modes
supported |
Feld Hell, PSK Hell,
FSK Hell, Duplo Hell, C/MT HELL, Morse (transmit only)
|
| Speeds
supported |
Standard speed plus
faster and slower by various factors |
| Sound
card mode |
8 bit samples at
11025 Hz rate |
| PTT
control |
Hamcom type interface,
VOX or serial radio interface |
| Receiver |
| Receive
algorithm |
Gray scale (256
levels) |
| Filter
Type |
Quadrature detector |
| Filter
Bandwidth |
Selectable from 75 to
500 Hz |
| Filter
downsampling |
Divide by 2 (0-5512.5
Hz) |
| Transmitter |
| Waveform
type |
sine-wave at 98% of
max volume,
zero crossing at each end of the pixel |
| Signal
filterning |
Raised cosine
envelope* |
| Bandwidth |
61.25 Hz* in Feld-Hell
mode, 105 Hz in PSK mode |
| Signal
generation |
Rendered wavetables |
| Fonts
supported |
Hellschreiber fonts,
Windows fonts,
Windows fonts with smoothed edges (greyscale fonts) |
* = only when using
Hellschreiber fonts
25-Dec-98: Version 0.0 - tests with taped
signals
01-Jan-99: Version 0.1 - first on-air QSO
[gap in my memory]
21-Feb-99: Version 0.8 - Added CW
28-Feb-99: Version 1.0 - Added C/MT and S/MT
Hell, Waterfall display, new user interface
13-Mar-99: Version 1.1 - Added FSK Hell,
FeldNar.Fon
20-Mar-99: Version 1.2 - FSK reworked,
self installer, Feldwide.fon, fixed lotsa bugs
28-Mar-99: Version 1.3 - FSK: full
negative / border only option, raised cosine, two selectable
shifts, middle gray value selectable, enabled +/- 3dB buttons;
CW: variable speed and correct dash/dot/pause values; INI
file: one directory placement bug, self creation with default
values; Waterfall: enabled/disable flag (for slow computers);
fixed status bar, enabled background rendering of font
wavetables.
5-Apr-99: Version 1.4 - Bugfix on
shapshot saving and on Waterfall display (you'll not see the
"ripple" effect anymore). Added waterfall update
refresh rate. Added new section for S/MT (still testing sorry).
Added FELD-DX.FON and FELDLITL.FON. Added new palette files.
Little code improvement.
11-Apr-99: Version 1.5 - Added FELDREAL.FON,
font used by real Hellschreiber machines (thanks to Koos PA0KDF
for the source); added new palette files (compressed and
expanded gamma cyans and a "swedish" one from YL2KF);
FSK: fixed bug on "border" fsk and added the option
"silence on idle" wich will not transmit the white
tone on idle or space character (so the TRX can have a breath);
increased the height of the waterfall display so it is easier
to tune in FSK; fixed the "downhill" bug wich
caused the text becaming hardly slanted on some situations;
fixed bug in CW so dit and dash now have the same pitch value
even in lower speeds; reprogrammed and eliminated most of
filter files: now Feld-Hell filters are fixed at 150 taps and
you can choose the bandwidth from a slider control in the
window; filter and palette settings are now saved in the
config file; the TX buffer have been reprogrammed so it
behaves better when you are sending words.
18-Apr-99: Version 1.6 - Selected font
and bias value are now saved on config file; bias isn't
resetted anymore if bandwidth changed; bandwidth changing
speeded up on slow computers; added (sort of) cw decoder (for
testing purposes only). Added menu option "Send opening
phrase" (key F12) wich will fill the buffer with "RRR
RRR DE ..." (so it has something to send while you're
typing in the buffer).
28-Apr-99: Version 1.7 - Six user
definable buttons where you can put your own text to send or
command to act (see $metacommands). A digital AGC wich will
track signal peaks and will make the text darker if fading or
RX desensitivity. CW decoder improvements with signal
amplitude plot and variable thereshold. Metacommands ($) for
beacon operations and other specialistic usage. A new font
set "FELDLOW.FON" which is bold in the vertical
direction for minimum bandwidth and more visibility in DX.
Special funny graphics characters on some fontsets (I will
not tell you where they are, it's an hidden function I use
for on-air jokes). "Idle character" option, lets
you define your own character to be sent when the TX is idle
(typically when you are completing a "word" from
the keyboard). The old "%%" shortcut option have
been eliminated. Added new speeds (4x and 8x slower).
Waterfall display is +6dB darker. Eliminated a bug in the
config file when bolded fonts was used.
7-May-99: Version 1.8 - Added two more
user definable buttons (for total of 8, anyway at least 800x600
resolution is needed to show them all). Added shortcut keys
to "tune signal" and "CQ" (F8 and F9
respectively). Added "Clear TX buffer" (CTRL+C key)
function. Corrected errors in some fontsets, and made them
loadable under Windows NT4.0. The maximum height of a
loadable font is now limited to 14 pixels. Fixed bugs in the
$metacommand routine and added $button1, $button2, ...
commands to send text defined by user definable buttons.
Added a hidden pop-up menu for sending the special characters
contained in the FELDLOW fontset. The "Send file"
command now keeps trace of last file sent in the config file;
it will also clear the file from line feeds/carriage returns.
Added a field for waterfall display bias value in the
preferences window. Reworked the C/MT routine which is almost
EVM compatible (not yet ready anyway). +/- 3dB button now
works in MT modes too. Added "Scope display"
function (key F6) which shows about 6 KHz of activity for
monitoring several channels at a time. Added a button for
instant snapshot of the current display into bitmap file.
Reworked icons and fixed a bug in DX mode with FSK. Added
cache technique for font rendering: it will not render fonts
at startup, but only when they are changed. Added callbook
database file (callbook.txt) and a nice "who is"
function directly via the menu.
19-May-99: Version 1.9 - Fixed bug on CW-ID.
Autosave bitmaps now defaults off. C/MT Hell almost completed
with five different speeds and bandwidth (one of which is EVM
compatible); it can send "smoothed fonts" as for
Feld-Hell and +/-3dB buttons now works in this mode too.
Fixed link to new Murray's Hellschreiber website. New
fontsets for S/MT Hell (SMTHELL.FON and SMT2.FON). Changed
the callbook file format so it can work with the html file
downloadable from the website. "Computer Speed"
option in preferences lets you choose the appropriate filter
for your machine speed; the new 300 taps filter set has very
sharp edges and a -100dB attenuation. Added a slider control
for the waterfall "zoom". DX mode (doubled columns)
does not render fonts anymore and has been added for C/MT
Hell too. There are two new metacommands: $DXON and $DXOFF
for controlling the DX mode via definable buttons or send-file.
German help file translation (V1.8) by DJ6SY Heinz.
13-Jun-99: Version 2.0 - Added a new
fuzzy mode: "MFSK Hell"! Shaped the output signal
with a raised cosine envelope when using fonts of the "Feld"
family. Added new font files "Feld Modern" and
"FeldVert". Changed the standard font file "FeldHell.fon"
by G3PLX so it will not conflict with the EVM Hellschreiber
program anymore. Improved the AGC routine, which is now more
"fluid". Small improvements in some fontsets. Fixed
a bug for which it was not possible to send characters like
"{" and "}". The flag "Append pause
character" is now saved in the config file. Added Czech
help file (translation by Josef OK2WO). First version of the
"Frequently Asked Questions" (FAQ) file. Added the
"Detect slow Typing" option. Added slanting
correction for inaccurate soundcards.
06-Jul-99: Version 2.1 - Bugfixes:
Deleted old option "Full Duplex soundcard" and
"Display own output". Bias won't go to zero in some
circumstances; CWID won't always return to previous transmit
mode - only to Feld-Hell; DX mode properly fixed for new
Duplo Hell mode; cursor positioned to last char when pressing
user definable buttons in "pause mode" (the mode
with *); filter now "on" by default. Slant
correction won't now generate noise when transmitting; the
"Load filter" option removed. "Append pause
character" more simply renamed "pause mode".
Corrected a buffer problem with "Detect slow typing"
option. It is not possible anymore to render fonts while
transmitting (causing program crash). It won't send the Idle
character in CW mode anymore. It won't hang if one tries to
send $C0 character. New features: New fuzzy
mode "Duplo Hell" (definitive version). It will
remember the window position and the maximized state after
each run (useful if you have other applications like loggers
etc.). AGC on/off button directly on the tool bar; single
button for start/stop of the virtual paper. New CW decoder
with explanation in the help file. Line wrapping option: you
can avoid broken text when the paper reaches the right margin
and a new line is generated. A small portion of the rightmost
text will be replicated on the new line. Slant correction
tool with tuning to standard time and frequency stations (like
WWV). F10 hotkey for CW-ID. Option "Beep when PTT off"
- a short "beep" from the computer's internal
speaker when the PTT has to be switched off (useful if you
are switching it manually - tells you the precise instant).
Italian help file translation. Option for calling your own
prefered log program via menu option. Other party callsign
hot-key facility (F11/F12) with automatic open/close standard
phrase. Speeded-up by letting the user select what wavetables
to load at startup. Better executable as it is compiled with
the new 4.0 release of the C++ Builder compiler :-).
4-Aug-99: Version 2.2 - Spanish help file
translation (by Raimon EA3EZO); Hotkey (CTRL+G) for log
program; F11 Key copies the other party callsign to clipboard
for pasting later in the log program; $NOQSO metacommand for
clearing other party callsign; Definable soundcard mixer
program; Redesigned "Scope mode" for CW meteor
scatter
7-Aug-99: Version 2.3 - Fixed a bug that
caused an "audio buffers" error when in CW mode
9-Aug-99: Version 2.4 - Added actual
frequency calculator
13-Aug-99: Version 2.5 - $Pn metacommand
for controlling the output power (useful in beacon mode); $DATEUTC
metacommand - will send the date referred to UTC time; Fixed
a bug in the actual frequency calculator; Added spanish Ñ (egne)
character on CW decoder (receive only); Stand-by option -
will release the com port and the soundcard for switching to
another program (i.e. PSK31); G3PPT's Slowfeld mode receiver;
Option for viewing the local copy of the Hellschreiber
callbook; Date and UTC time displayed in the status bar
16-Aug-99: Version 2.6: PTT support for
WD5GNR drivers for PSKGNR; Options for quick loading the PSK31
program; Czech help file updated
25-Sep-99: Version 2.7: New features: New
mode "PSK-Hell", using polar reversal shift keying
at 105 baud rate. New tone detection algorythm using "quadrature
detector" in place of FIR filters. This give us also
variable filter bandwidth.Redesigned C/MT Hell using a 5x5
character matrix. Now is fast and clear to see. New AGC
routine that keeps constant the contrast of the text, with
selectable response. New working sample rate of 11025 Hz on
transmit and 5512.5 Hz on receive for minimal CPU load.
Faster "refresh" of the RX display. Option "force
uppercase letter" for writing in uppercase regarderless
of the caps lock state. Improved the waterfall display with
also smooth and negative colors (for a PSK31 like display).
New fontsets: Feld7x7 and Feld7x7n.fon. Define button "on
the fly" with four more buttons. Bugfixes / small
updates: Faster CTRL+C key (clear TX buffer). Preference
shortcut button on the toolbar. Changed the +/- 3db buttons
into a "RX Gain" slider control. DX mode now always
off by default. Japanese help file translation. Spanish help
file updated. Scope display at 2048 points resolution fixed.
CW decoder removed (eventually split into another program).
23-dec-99: Version 2.8: Hotkey for
switching to MT63. Spanish help file updated
24-Jan-200: Version 2.9: CTRL+FKeys macro
buttons (and with menu). CQ Button on front panel. New
waterfall display (some option of the old one no longer
exists). Old "scope display" eliminated. Rearranged
some options in setup window. Small code improvements.
BlockLenMultiplier variabile in .ini file for controlling/reducing
the CPU load (and program "fluidity" response).
04-Feb-2000: Version 3.0 beta: Big
waterfall display, variable sidetone frequency, point-and-click
operations. Logbook window with export ADIF files (.adi). $OTHERNAME
metacommand. Raised cosine envelope on FSK, DUPLO, CW. Raised
cosine envelope even on non Feld-Hell fonts. Improved the
readability of DUPLO. C/MT Hell mode compatible with the EVM
Version (requires fast cpu). No more "rendering" of
wavetables. Enlarged labels above macro buttons. Small code
improvements. What have been eliminated: Variable speeds, 490
Hz shift on DUPLO and PSK, PSK Clarifier, "Bias"
control, Old 5 tones C/MT Hell.
23-Feb-2000: Version 3.0 final.
Communication with Logger program by Bob Furzer K4CY.
Improved sensitivity of PSK-Hell. Improved "docking"
of logbook window. Bugfixes from 3.0e.
28-Feb-2000: Version 3.1: CQ button
definable; "Send open/close phrase" is now called
"Send pre/postamble phrase"; Preamble and postamble
string definable (F12 key); Updated spanish and czech help
files; PSK-Hell (245 baud) available in menu "mode"
(this mode finished the its test phase);
16-Mar-2000: Version 3.2: User interface
improvements. Button for sending a two carriers signal for
visual IMD checks. Added foreign language characters (in
Feldnarr.fon only). Fixed space between letters of CW-ID and
made CW signal less "smooth". Fixed menu item PSK245
baud and eliminated the old option "reduce power on idle".
Added metacommand $IMD and $PSK245
17-Mar-2000: Version 3.3: New mode Duplo
PSK.Changed the behaviour of "idle character": now
if there are at leat four characters in the TX buffer they
will be sent instead of waiting for a word to be completed (this
helps if you are writing quite long words). Font in use
displayed in the status bar. Better contrast of own
transmission in RX display
1-Apr-2000: Version 3.4: Waterfall
display Logarithmic or Linear (coloured respectively white on
black and black on white). Minimun number of character in TX
buffer selectable. SSB-PSK Hell (experimental modes). Minor
bugs removed
8-Apr-2000: Version 3.5a: Reorganization
of Hell modes. Duplo-PSK has been deleted (didn't show
significant improvements). FSK-Hell replaced by the
experimental SSB-PSK wich is now called FM-Hell (both 105 and
245 baud versions are provided).
01-May-2000: Version 3.5b: [omitted]
03-May-2000: Version 3.5c: [omitted]
05-Aug-2000: Version 3.6: New user interface (more similar to
Stream program) with more usable space and self-sizing macro buttons. Option
for calling the Stream program without closing the program (CTRL+H). Flag in
the preferences window for having ADIF logfile's date/time in UTC format
rather than local format. Customizable sidetone center Frequency (right
mouse click). Satellite full duplex mode. FM-Hell shift tester. Better default FFT
resolution. Actual frequency calculator reads the current sidetone value.
19-Jan-2001: Version 3.7: Added french help file. Added option for
meteorscatter operations (5X and 9X speed).
23-Mar-2001: Version 3.8: Reitroduced 1/8X speed for troposcatter
QSOs. New meteorscatter mode 10X speed featuring a special version of the
Duplo-Hell.
[a long 3 years pause]
2-Feb-2004: Version 4.0: A new updated version which runs under
Windows XP. Soundcard selectable for both transmit and receive.
Waterfall display sizeable with a "splitter" control.
IZ8BLY Hellschreiber for 32 bit
windows platform
© 1998-2004 Nino Porcino, nino.porcino@tin.it
